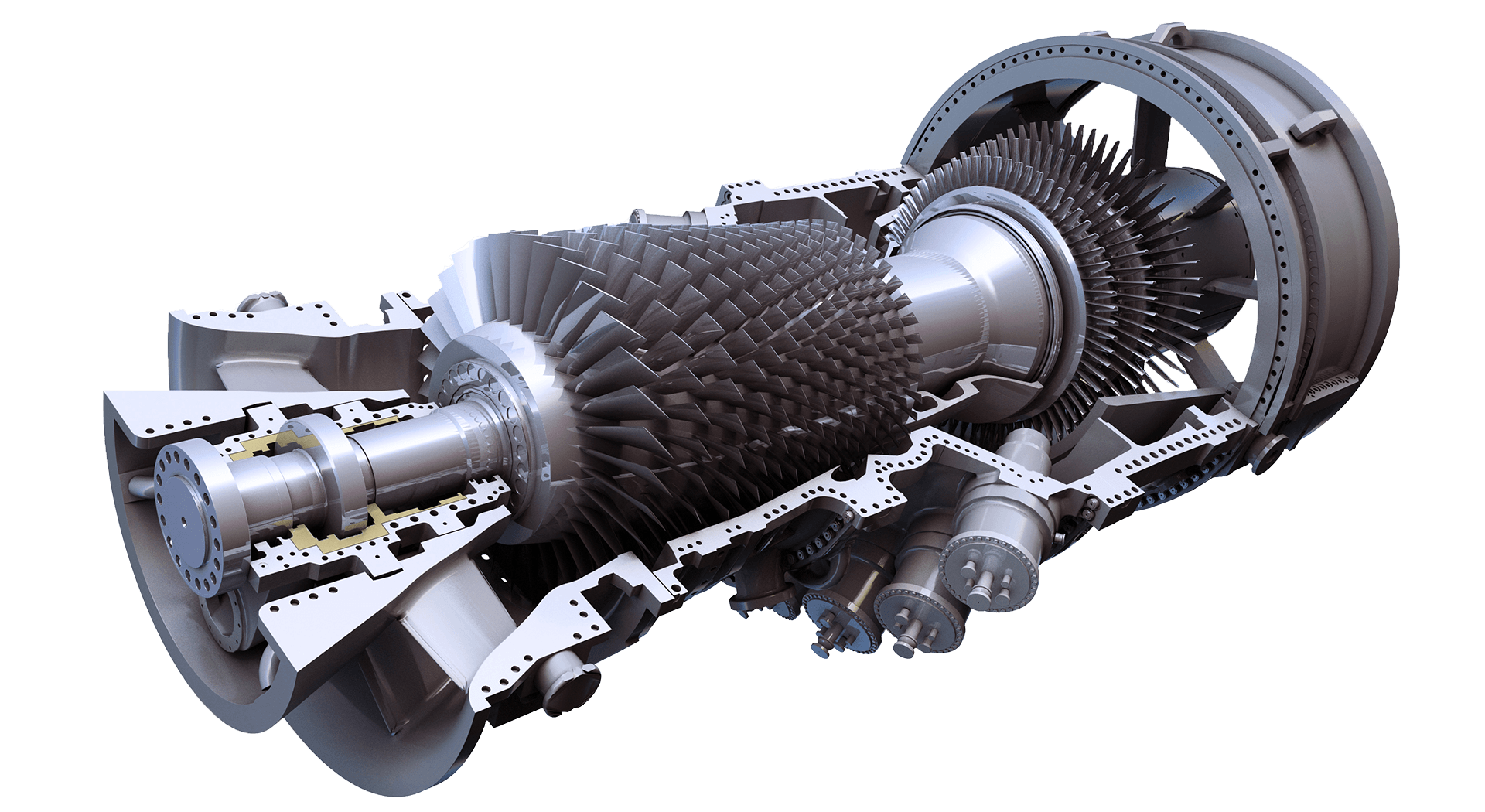
In today’s energy landscape, the demand for clean, reliable, and efficient power generation technologies is paramount. Gas turbines have emerged as a leading solution, offering a versatile and sustainable means of producing electricity.
This article delves into the workings of gas turbine power generation technologies, highlighting their environmental benefits, reliability, and efficiency.
The Basics of Gas Turbines
Gas turbines operate on the principle of converting the energy stored in fuel into mechanical energy, which is then transformed into electrical energy. Unlike traditional steam turbines, gas turbines rely on combustion rather than steam to drive the turbine blades.
Environmental Benefits
One of the primary advantages of gas turbine technology is its relatively low environmental impact. Modern gas turbines employ advanced combustion techniques and emissions control systems, resulting in reduced greenhouse gas emissions compared to coal-fired power plants. Additionally, gas turbines can run on a variety of fuels, including natural gas, biogas, and hydrogen, further enhancing their environmental credentials.
Reliability
Gas turbine power plants are renowned for their reliability and uptime. These systems are engineered with redundancy and fail-safe mechanisms to ensure continuous operation even in adverse conditions. Furthermore, gas turbines boast rapid startup times, making them ideal for meeting fluctuating electricity demands and providing grid stability.
Efficiency
Efficiency is a critical factor in power generation, and gas turbines excel in this regard. Combined cycle power plants, which integrate gas turbines with steam turbines, can achieve thermal efficiencies exceeding 60%. This high efficiency not only reduces fuel consumption but also lowers operating costs and greenhouse gas emissions.
Applications
Gas turbine power generators utilize technology across diverse sectors, encompassing utilities, industrial facilities, and distributed generation sites. Their versatility and modular design make them suitable for both baseload and peaking power generation, as well as for combined heat and power (CHP) applications.
Future Outlook
As the global energy transition accelerates, gas turbine technology is expected to play a vital role in the transition to a cleaner and more sustainable energy future. Ongoing research and development efforts focus on enhancing efficiency, reducing emissions, and expanding the use of alternative fuels such as green hydrogen.
Grid Stability
Gas turbine power plants play a crucial role in maintaining grid stability, especially in regions with high renewable energy penetration. Their fast response times and ability to ramp up or down quickly complement the intermittent nature of renewable energy sources like wind and solar, helping to balance supply and demand and prevent blackouts.
Decentralization
Gas turbine technologies support the trend towards decentralized power generation by enabling distributed energy resources. Modular gas turbine units can be deployed at various locations, reducing transmission losses and enhancing energy resilience. This decentralization also promotes energy independence and security, particularly in remote or underserved areas.
Conclusion
Clean, reliable, and efficient, gas turbine power generation technologies represent a cornerstone of modern energy infrastructure. With their ability to provide flexible, low-emission electricity generation, gas turbines are poised to remain a key player in the global energy mix for years to come.
As we navigate the challenges of climate change and energy security, gas turbines stand ready to power the transition to a sustainable energy future.